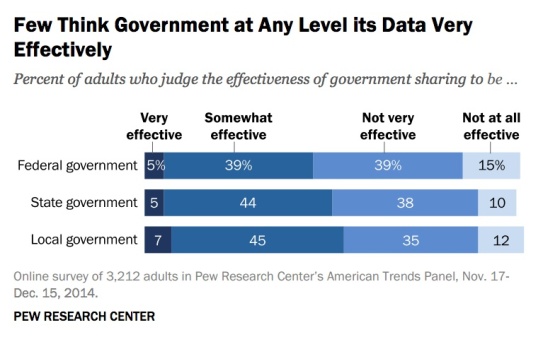
Today, the Center for Effective Government released a scorecard for access to information from the 15 United States federal government agencies that received the most Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) requests, focusing upon an analysis of their performance in 2013.
The results of the report (PDF) for the agencies weren’t pretty: if you computed a grade point average from this open government report card (and I did) the federal government would receive a D for its performance. 7 agencies outright failed, with the State Department receiving the worst grade (37%).
The grades were based upon:
- How well agencies processed FOIA requests, including the rate of disclosure, fullness of information provided, and timeliness of the response
- How well the agencies established rules of information access, including the effectiveness of agency polices on withholding information and communications with requestors
- Creating user-friendly websites, including features that facilitate the flow of information to citizens, associated online services, and up-to-date reading rooms
The report is released at an interesting historic moment for the United States, with Sunshine Week just around the corner. The United States House of Representatives just unanimously passed a FOIA Reform Act that is substantially modeled upon the Obama administration’s proposals for FOIA reforms, advanced as part of the second National Open Government Action Plan. If the Senate takes up that bill and passes it, it would be one of the most important, substantive achievements in institutionalizing open government beyond this administration.
The Citizens for Responsibility and Ethics in Washington have disputed the accuracy of this scorecard, based upon the high rating for the Department of Justice. CREW counsel Anne Weismann:
It is appropriate and fair to recognize agencies that are fulfilling their obligations under the FOIA. But CEG’s latest report does a huge disservice to all requesters by falsely inflating DOJ’s performance, and ignoring the myriad ways in which that agency — a supposed leader on the FOIA front — ignores, if not flouts, its obligations under the statute.
Last Friday, I spoke with Sean Moulton, the director of open government policy at the Center for Effective Government, about the contents of the report and the state of FOIA in the federal government, from the status quo to what needs to be done. Our interview, lightly edited for content and clarity, follows.
What was the methodology behind the report?
Moulton: Our goal was to keep this very quantifiable, very exact, and to try and lay out some specifics. We thought about what the components were necessary for a successful FOIA program. The processing numbers that come out each year are a very rich area for data. They’re extremely important: if you’re not processing quickly and releasing information, you can’t be successful, regardless of other components.
We did think that there are two other areas that are important. First, online services. Let’s face it, the majority of us live online in a big way. It’s a requirement now for agencies to be living there as well. Then, the rules. They’re explained to the agencies and the public, in how they’re going to do things when they get a request. A lot of the agencies have outdated rules. Their current practices may be different, and they may be doing things that the rules don’t say they have to, but without them, they may stop. Consistent rules are essential for consistent long term performance.
A few months back, we released a report that laid out what we felt were best practices for FOIA regulations. We went through a review of dozens of agencies, in terms of their FOIA regulations, and identified key issues, such as communicating with the requester, how you manage confidential business information, how you handle appeals, and how you handle timelines. Then we found inside existing regulations the best ways this was being handled. It really helped us here, when we got to the rules. We used that as our roadmap. We knew agencies were already doing these things, and making that commitment. The main thing we measured under the rules were the items from that best practices report that were common already. If things were universal, we didn’t want to call a best practice, but a normal practice.
Is FOIA compliance better under the Obama administration, more than 4 years after the Open Government Directive?
Moulton: In general, I think FOIA is improving in this administration. Certainly, the administration itself is investing a great deal of energy and resources in trying to make greater improvements in FOIA, but it’s challenging. None of this has penetrated into national security issues.
I think it’s more of a challenge than the administration thought it would be. It’s different from other things, like open data or better websites. The FOIA process has become entrenched. The biggest open government wins were in areas where they were breaking new ground. There wasn’t a culture or way of doing this or problems that were inherited. They were building from the beginning. With FOIA, there was a long history. Some agencies may see FOIA as some sort of burden, and not part of their mission. They may think of it as a distraction from their mission, in fact. When the Department of Transportation puts out information, it usually gets used in the service of their mission. Many agencies haven’t internalized that.
There’s also the issue of backlogs, bureaucracy, lack of technology or technology that doesn’t work that well — but they’re locked into it.
What about redaction issues? Can you be FOIA compliant without actually honoring the intent of the request?
Moulton: We’re very aware of this as well. The data is just not there to evaluate that. We wish it was. The most you get right now is “fully granted” or “partly granted.” That’s incredibly vague. You can redact 99% or 1% and claim it’s partially redacted, either way. We have no indicator and no data on how much is being released. It’s frustrating, because something like that would help us get a better sense on whether agencies would benefit would new policies
We do know that the percentage of full grants has dropped every year, for 12 years, from the Clinton administration all the way through the Bush administration to today. It’s such a gray area. It’s hard to say whether it’s a terrible thing or a modest change.
Has the Obama administration’s focus on open government made any difference?
Moulton: I think it has. There were a couple of agencies that got together on FOIA reform. The EPA led the team, with the U.S. National Archives and the Commerce Department, to build a new FOIA tool. The outward-facing part of the tool enables a user to go to a single spot, request and track it. Other people could come and search FOIA’ed documents. Behind the scenes, federal workers could use the tool to forward requests back and forth. This fits into what the administration has been trying to do, using technology better in government
Another example, again at the EPA, is where they’ve put together a proactive disclosure website. They got a lot of requests, like if there are inquiries about properties, environmental history, like leaks and spills, and set up a site where you could look up real estate. They did this because they went to FOIA requests and see what people wanted. That has cut down their requests to a certain percentage.
Has there been increasing FOIA demand in recent years, affecting compliance?
Moulton: I do think FOIA requests have been increasing. We’ll see what this next year of data shows. We have seen a pretty significant increase, after a significant decrease in the Bush administration. That may be because this administration keeps speaking about open government, which leads to more hopeful requestors. We fully expect that in 2013, there will be more requests than the prior year.
DHS gets the biggest number of all, but that’s not surprising when we look at the size of it. It’s second biggest agency, after Defense, and the biggest domestic facing agency. when you start talking about things like immigration and FEMA, which go deep into communities and people’s lives, in ways that have a lot impact, that makes sense.
What about the Department of Justice’s record?
Moulton: Well, DoJ got the second highest rating, but we know they have a mixed record. There are things you can’t measure and quantify, in terms of culture and attitude. I do know there were concerns about the online portal, in terms of the turf war between agencies. There were concerns about whether the tech was flexible, in terms of meeting all agency needs. If you want to build a government-wide tool, it needs to have real flexibility. The portal changed the dialogue entirely
Is FOIA performance a sufficient metric to analyze any administration’s performance on open government?
Moulton: We should step back further and look at the broader picture, if we’re going to talk about open government. This administration has done things, outside of FOIA, to try to open up records and data. They’ve built better online tools for people to get information. You have to consider all of those things.
Moulton: That’s a good example. One thing this administration did early on is to identify social media outlets. We should be going there. We can’t make citizens come to us. We should go to where people are. The administration pushed early on that agencies should be able to use Tumblr and Twitter and Facebook and Flickr and so on.
Is this social media use “propaganda,” as some members of the media have suggested?
Moulton: That’s really hard to decide. I think it can result in that. It has the potential to be misused to sidestep the media, and not have good interaction with the media, which is another important outlet. People get a lot of their information from the media. Government needs to have good relationship.
I don’t think that’s the intention, though, just as under Clinton, when they started setting up websites for the first time. That’s what the Internet is for: sharing information. That’s what social media can be used for, so let’s use what’s there.