Today, a new survey released by the Pew Research Internet and Life Project provided one of the most comprehensive snapshots into the attitudes of the American public towards open data and open government to date. In general, more people surveyed are guardedly optimistic about the outcomes and release of open data, although that belief does vary with their political views, trust in government, and specific areas. (Full disclosure: I was consulted by Pew researchers regarding useful survey questions to pose.)

“Trust in government is the reference that people bring to their answers on open government and open data,” said John Horrigan, the principal researcher on the survey, in an interview. “That’s the frame of reference people bring. A lot of people still aren’t familiar with the notion, and because they don’t have a framework about open data, trust dominates, and you get the response that we got.”
While majorities of the American public use applications and services that use government data, from GPS to weather to transit to health apps, relatively few are aware that data produced and released by government drives them.
“The challenge for activists or advocates in this space will be to try to make the link between government data and service delivery outcomes,” said Horrigan. “If the goals are to make government perform better and maybe reverse the historic tide of lowered trust, then the goal is to make improvements real in delivery. If this is framed just as argument over data quality, it would go into an irresolvable back and forth into the quality of government data collection. If you can cast it beyond whether unemployment statistics are correct or not but instead of how government services improve or saved money, you have a chance of speaking to wether government data makes things better.”
The public knowledge gap regarding this connection is one of the most important points that proponents, advocates, journalists and publishers who wish to see funding for open data initiatives be maintained or Freedom of Information Act reforms pass.
“I think a key implication of the findings is that – if advocates of government data initiatives hope that data will improve people’s views about government’s efficacy – efforts by intermediaries or governments to tie the open data/open government to the government’s collection of data may be worthwhile,” said Horrigan. “Such public awareness efforts might introduce a new “mental model” for the public about what these initiatives are all about. Right now, at least as the data for this report suggests, people do not have a clear sense of government data initiatives. And that means the context for how they think about them has a lot to do with their baseline level of trust in the government – particularly the federal government.”
Horrigan suggested thinking about this using a metaphor familiar to anyone who’s attended a middle school dance.
“Because people do engage with the government online, just through services, it’s like getting them on a big dance floor,” he suggested. “They’re on the floor, where you want them, but they’re on the other part of it. They don’t know that there’s another part of the dance that they’d like to see or be drawn to that they’d want to be in. There’s an opportunity to draw them. The good news that they’re on the dance floor, the bad news is they don’t know about all of it. Someone might want to go over and talk to them an explain that if you go over here you might have a better experience.”
Following are 13 more key insights about the public’s views regarding the Internet, open data and government. For more, make sure to read the full report on open government data, which is full of useful discussion of its findings.
One additional worth noting before you dive in: this survey is representative of American adults, not just the attitudes of people who are online. “The Americans Trends Panel was recruited to be nationally representative, and is weighted in such a way (as nearly all surveys are) to ensure responses reflect the general population,” said Horrigan. “The overall rate of internet use is a bit higher than we typically record, but within the margin of error. So we are comfortable that the sample is representative of the general population.”
Growing number of Americans adults are using the Internet to get information and data
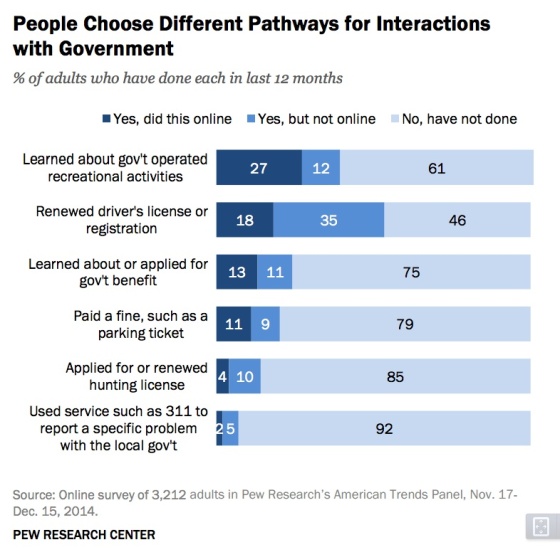
While Pew cautions that the questions posed in this survey are different from another conducted in 2010, the trend is clear: the way citizens communicate with government now includes the Internet, and the way government communicates with citizens increasingly includes digital channels. That use now includes getting information or data about federal, state and local government.
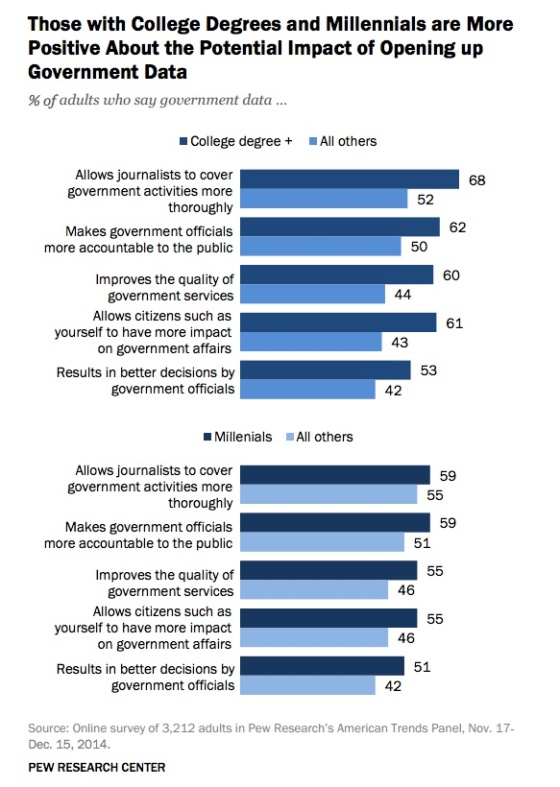
College-educated Americans and millennials are more hopeful about open data releases
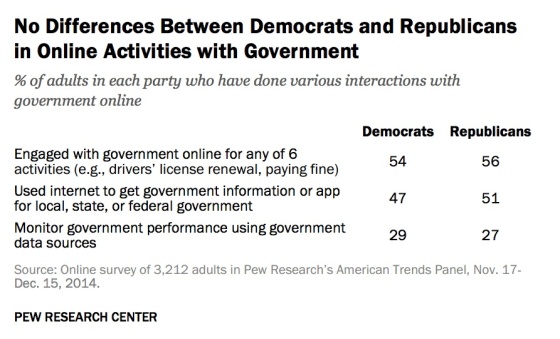
Despite disparities in trust and belief in outcomes, there is no difference in online activities between members of political parties
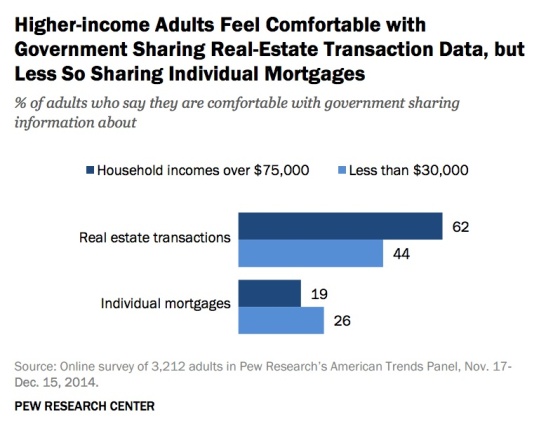
Wealthier Americans are comfortable with open data about real estate transactions but not individual mortgages
This attitude is generally true across all income levels.
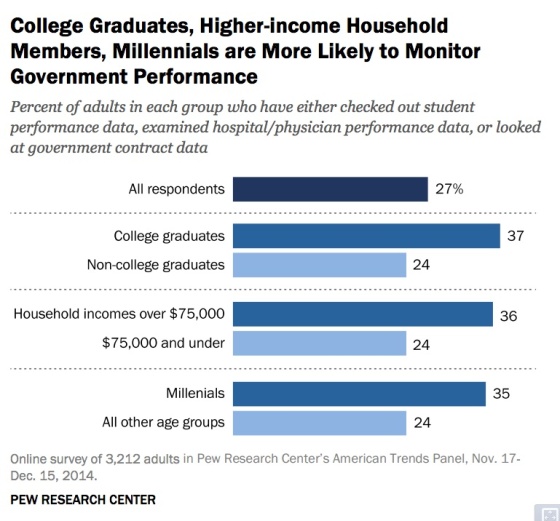
College graduates, millennials and higher-income adults are more likely to use data to monitor government performance
About a third of college grads, young people and wealthy Americans have checked out performance data or government contracting data, or about 50% more than other age groups, lower income or non-college grads.
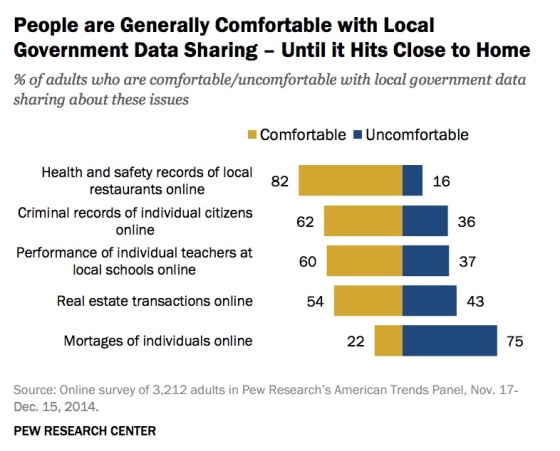
The ways American adults interact with government services and data digitally are expanding
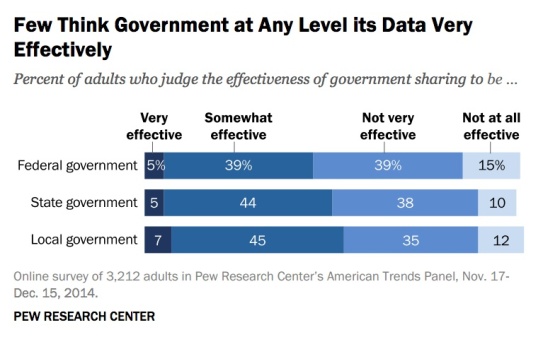
But very few American adults think government data sharing is currently very effective:
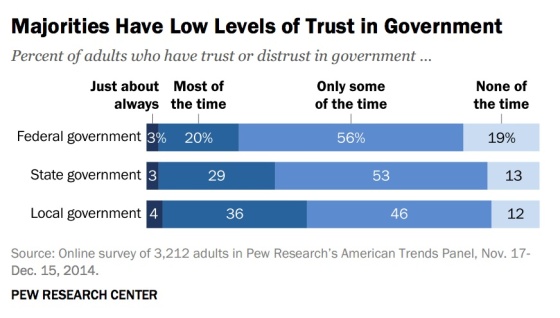
A small minority of Americans, however, have a great deal of trust in federal government at all:
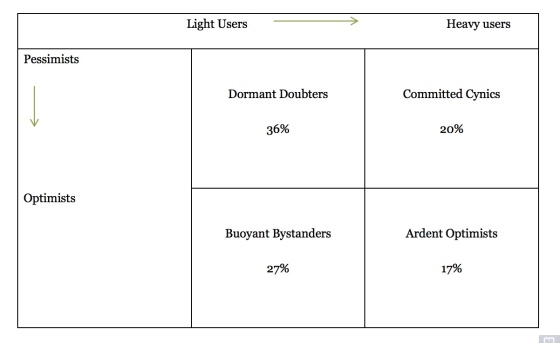
In fact, increasing individual use of data isn’t necessarily correlated with belief in positive outcomes:
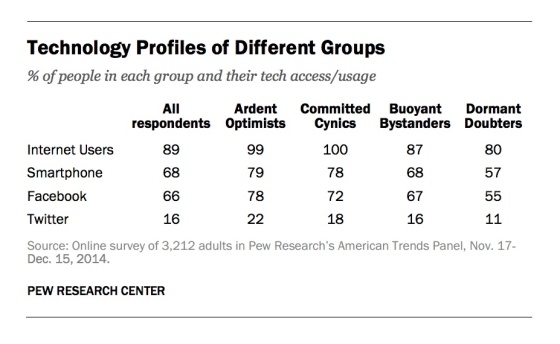
Pew grouped the 3,212 respondents into four quadrants, seen below, with a vertical axis ranging from optimism to skepticism and a horizontal axis that described use. Notably, more use of data doesn’t correlate to more belief in positive outcomes.
“In my mind, you have to get to the part of the story where you show government ran better as a result,” said Horrigan. “You have to get to a position where these stories are being told. Then, at least, while you’re opening up new possibilities for cynicism or skepticism, you’re at least focused on the data as opposed to trust in government.”
Instead…
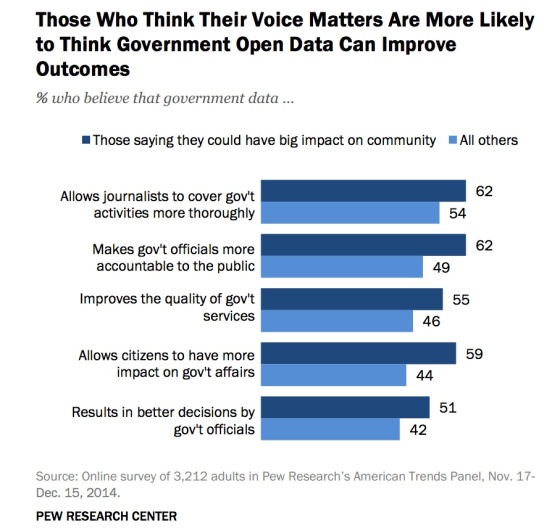
Belief in positive outcomes from the release of open data is correlated with a belief that your voice matters in this republic:
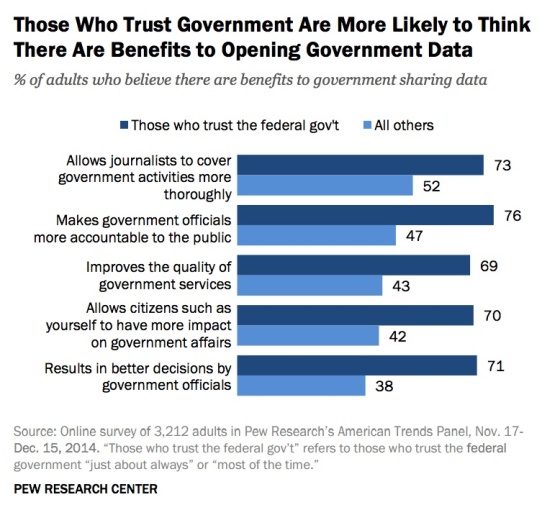
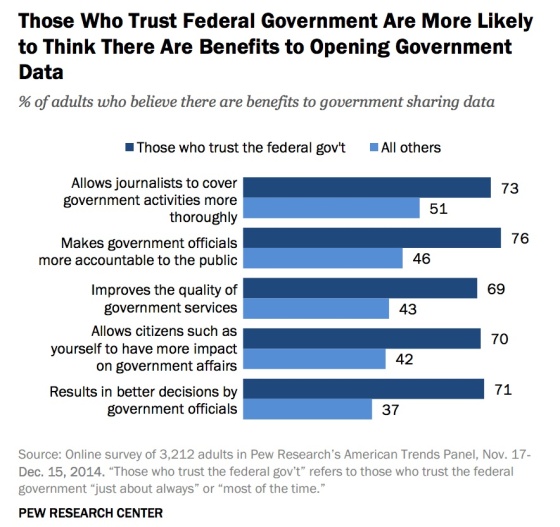
If you trust the federal government, you’re more likely to see the benefit in open data:
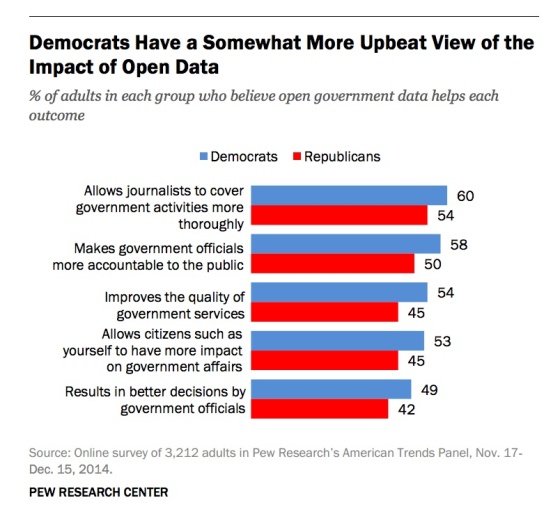
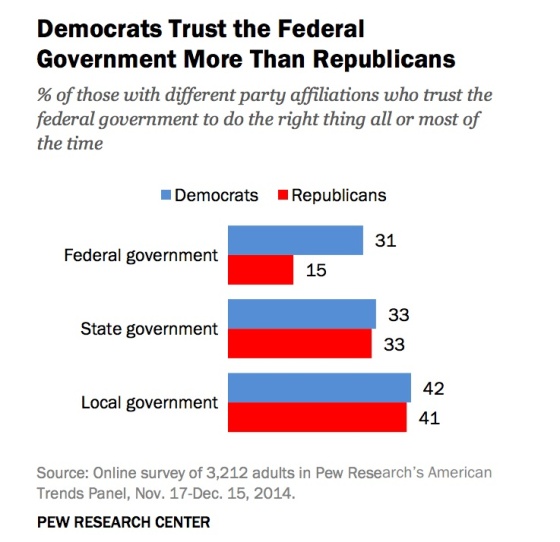
But belief in positive outcomes from the release of open data is related to political party affiliation:
Put simply, Democrats trust the federal government more, and that relates to how people feel about open data released by that government.
Political party has an impact upon the view of open data in the federal government
One challenge is that if President Barack Obama says “open data” again, he may further associate the release of government data with Democratic policies, despite bipartisan support for open government data in Congress. If a Republican is elected President in November 2016, however, this particular attitude may well shift.
“That’s definitely the historic pattern, tracked over time, dating to 1958,” said Horrigan, citing a Pew study. “If if holds and a Republican wins the White House, you’d expect it to flip. Let’s say that we get a Republican president and he continues some of these initiatives to make government perform better, which I expect to be the case. The Bush administration invested in e-government, and used the tools available to them at the time. The Obama administration picked it up, used the new tools available, and got better. President [X] could say this stuff works.”
The unresolved question that we won’t know the answer to until well into 2017, if then, is whether today’s era of hyper-partisanship will change this historic pattern.
There’s bipartisan agreement on the need to use government data better in government. Democratss want to improve efficiency and effectiveness, Republicans want to do the same, but often in the context of demonstrating that programs or policies are ineffective and thereby shrink government. If the country can rise about partisan politics to innovate government, awareness of the utility of releases will grow, along with support for open data will grow.
“Many Americans are not much attuned to government data initiatives, which is why they think about them (in the attitudinal questions) through the lens of whether they trust government,” said Horrigan. “Even the positive part of the attitudinal questions (i.e., the data initiatives can improve accountability) has a dollop of concern, in that even the positive findings can be seen as people saying: ‘These government data initiatives might be good because they will shine more light on government – which really needs it because government doesn’t perform well enough.’ That is an opportunity of course – especially for intermediaries that might, through use of data, help the public understand how/whether government is being accountable to citizens.”
That opportunity is cause for hope.
“Whether it is ‘traditional’ online access for doing transactions/info searches with respect to government, or using mobile apps that rely on government data, people engage with government online, “said Horrigan. “That creates the opportunity for advocates of government data initiatives to draw citizens further down the path of understanding (and perhaps better appreciating) the possible impacts of such initiatives.”



Pingback: Half empty or half full? Mixed reactions to Pew research on open data and open government | E Pluribus Unum