Citizensourcing and open innovation can work in the public sector, just as crowdsourcing can in the private sector. Around the world, the use of prizes to spur innovation has been booming for years. The United States of America has been significantly scaling up its use of prizes and challenges to solving grand national challenges since January 2011, when, President Obama signed an updated version of the America COMPETES Act into law.
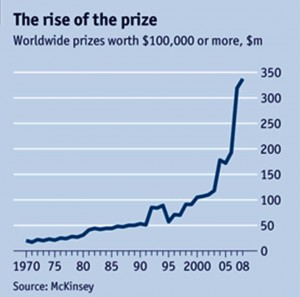
According to the third congressionally mandated report released by the Obama administration today (PDF/Text), the number of prizes and challenges conducted under the America COMPETES Act has increased by 50% since 2012, 85% since 2012, and nearly six-fold overall since 2011. 25 different federal agencies offered prizes under COMPETES in fiscal year 2013, with 87 prize competitions in total. The size of the prize purses has also grown as well, with 11 challenges over $100,000 in 2013. Nearly half of the prizes conducted in FY 2013 were focused on software, including applications, data visualization tools, and predictive algorithms. Challenge.gov, the award-winning online platform for crowdsourcing national challenges, now has tens of thousands of users who have participated in more than 300 public-sector prize competitions. Beyond the growth in prize numbers and amounts, Obama administration highlighted 4 trends in public-sector prize competitions:
- New models for public engagement and community building during competitions
- Growth software and information technology challenges, with nearly 50% of the total prizes in this category
- More emphasis on sustainability and “creating a post-competition path to success”
- Increased focus on identifying novel approaches to solving problems
The growth of open innovation in and by the public sector was directly enabled by Congress and the White House, working together for the common good. Congress reauthorized COMPETES in 2010 with an amendment to Section 105 of the act that added a Section 24 on “Prize Competitions,” providing all agencies with the authority to conduct prizes and challenges that only NASA and DARPA has previously enjoyed, and the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP), which has been guiding its implementation and providing guidance on the use of challenges and prizes to promote open government.
“This progress is due to important steps that the Obama Administration has taken to make prizes a standard tool in every agency’s toolbox,” wrote Cristin Dorgelo, assistant director for grand challenges in OSTP, in a WhiteHouse.gov blog post on engaging citizen solvers with prizes:
In his September 2009 Strategy for American Innovation, President Obama called on all Federal agencies to increase their use of prizes to address some of our Nation’s most pressing challenges. Those efforts have expanded since the signing of the America COMPETES Reauthorization Act of 2010, which provided all agencies with expanded authority to pursue ambitious prizes with robust incentives.
To support these ongoing efforts, OSTP and the General Services Administration have trained over 1,200 agency staff through workshops, online resources, and an active community of practice. And NASA’s Center of Excellence for Collaborative Innovation (COECI) provides a full suite of prize implementation services, allowing agencies to experiment with these new methods before standing up their own capabilities.
Sun Microsystems co-founder Bill Joy famously once said that “No matter who you are, most of the smartest people work for someone else.” This rings true, in and outside of government. The idea of governments using prizes like this to inspire technological innovation, however, is not reliant on Web services and social media, born from the fertile mind of a Silicon Valley entrepreneur. As the introduction to the third White House prize report notes:
“One of the most famous scientific achievements in nautical history was spurred by a grand challenge issued in the 18th Century. The issue of safe, long distance sea travel in the Age of Sail was of such great importance that the British government offered a cash award of £20,000 pounds to anyone who could invent a way of precisely determining a ship’s longitude. The Longitude Prize, enacted by the British Parliament in 1714, would be worth some £30 million pounds today, but even by that measure the value of the marine chronometer invented by British clockmaker John Harrison might be a deal.”
 Centuries later, the Internet, World Wide Web, mobile devices and social media offer the best platforms in history for this kind of approach to solving grand challenges and catalyzing civic innovation, helping public officials and businesses find new ways to solve old problem. When a new idea, technology or methodology that challenges and improves upon existing processes and systems, it can improve the lives of citizens or the function of the society that they live within.
Centuries later, the Internet, World Wide Web, mobile devices and social media offer the best platforms in history for this kind of approach to solving grand challenges and catalyzing civic innovation, helping public officials and businesses find new ways to solve old problem. When a new idea, technology or methodology that challenges and improves upon existing processes and systems, it can improve the lives of citizens or the function of the society that they live within.
“Open innovation or crowdsourcing or whatever you want to call it is real, and is (slowly) making inroads into mainstream (i.e. non high-tech) corporate America,” said MIT principal research professor Andrew McAfee, in an interview in 2012.” P&G is real. Innocentive is real. Kickstarter is real. Idea solicitations like the ones from Starbucks are real, and lead-user innovation is really real.”
Prizes and competitions all rely upon the same simple idea behind the efforts like the X-Prize: tapping into the distributed intelligence of humans using a structured methodology. This might include distributing work, in terms of completing a given task or project, or soliciting information about how to design a process, product or policy.
Over the past decade, experiments with this kind of civic innovation around the world have been driven by tight budgets and increased demands for services, and enabled by the increased availability of inexpensive, lightweight tools for collaborating with connected populations. The report claimed that crowdsourcing can save federal agencies significant taxpayer dollars, citing an example of a challenge where the outcome cost a sixth of the estimated total of a traditional approach.
One example of a cost-effective prize program is the Medicaid Provider Screening Challenge that was offered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) as part of a pilot designed in partnership with states and other stakeholders. This prize program was a series of software development challenges designed to improve capabilities for streamlining operations and screening Medicaid providers to reduce fraud and abuse. With a total prize purse of $500,000, the challenge series is leading to the development of an open source multi-state, multi-program provider screening shared-service software program capable of risk scoring, credential validation, identity authentication, and sanction checks, while lowering the burden on providers and reducing administrative and infrastructure expenses for states and Federal programs. CMS partnered with the NASA Center of Excellence for Collaborative Innovation (COECI), NASA’s contractor Harvard Business School, Harvard’s subcontractor TopCoder, and the State of Minnesota. The State of Minnesota is working on full deployment of the software, and CMS is initiating a campaign to encourage other states to leverage the software. COECI estimates that the cost of designing and building the portal through crowdsourcing was one-sixth of what the effort would have cost using traditional software development methods. Through the success of this and subsequent
challenges, CMS is attempting to establish a new paradigm for crowdsourcing state and Federal information technology (IT) systems in a low-cost, agile manner by opening challenges to new players, small companies, and talented individual developers to build solutions which can “plug and play” with existing legacy systems or can operate in a shared, cloud-based environment.
As is always the nature of experiments, many early attempts failed. A few have worked and subsequently grown into sustainable applications, services, data sources, startups, processes and knowledge that can be massively scaled. Years ago, Micah Sifry predicted that the “gains from enabling a culture of open challenges, outsider innovation and public participation” in government were going to be huge. He was right.
Linked below are the administration’s official letters to the House and Senate, reporting the results of last year’s prizes.
COMPETES FY2013PrizesReport HOUSE Letter (PDF)/COMPETES FY2013PrizesReport HOUSE Letter (Text)
COMPETES FY2013 PrizesReport SENATE Letter (PDF)/COMPETES FY2013 PrizesReport SENATE Letter (Text)
[Image Credit: NASA SDO. Context: Solar flare predictive algorithm challenge]


Pingback: United States federal government use of crowdso...