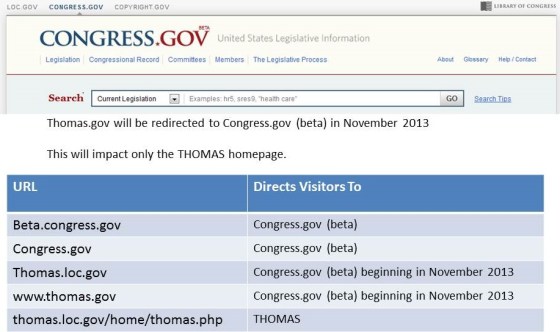
On November 19th, Thomas.gov, the venerable website of the United States Congress, will begin to redirect visitors to Congress.gov. The new site, which launched in beta in September 2012, will become the primary governmental resource for the text of legislation, past, present and future, along with reports from committees, speeches from the floor of Congress and cost estimates from the Congressional Budget Office.
While the official announcement was made today by the Library of Congress, Thomas.gov’s custodian, leading headlines about Congress trading in the new Congress.gov and a note in Roll Call, the transition from THOMAS.gov to Congress.gov has been going on all fall, including updates to the new site and launching the Constitution Annotated and associated app.
THOMAS is centuries old, at least as measured in terms of Internet time. Launched in January of 1995, Thomas.gov was one of the first 23,000 websites to go online. When it went live the Internet had a worldwide user base of less than 40 million people, the majority of whom surfed the young World Wide Web using Mosaic and Netscape, checked their email on Eudora and dialed in on America Online. Watch the video below to get a sense of what life was like online nearly two decades ago.
Today, Thomas.gov receives, on average, 10 million visits every year, although I suspect many of those visits come from wonky repeat customers in or around the District of Columbia. I have no servers logs to prove that one way or another, but THOMAS has long been alternately beloved of or bemoaned by Congressional staffers and correspondents, all of whom have had to rely upon its increasingly creaky infrastructure for nearly two decades as the national repository of legislation and reports. So, too, have millions of Americans around the rest of the country who want to read proposed bills.
While incremental improvements to search and sharing in recent years have improved the site, for a decade people interested in tracking Congress have increasingly turned to sites like Govtrack or the New York Times for data created by scraping THOMAS. What does that mean, in practice? While Congress.gov will be official source of information, until its operators move to act as a platform for legislative data instead of a portal for legislative information. Open government advocates have been calling for the release of bulk legislative data for many years, culminating in frustration this September when a Library of Congress cost estimate acknowledged that Congress.gov “was not designed specifically to facilitate the extraction of the data as XML documents for bulk download.”
Putting the issue of bulk data aside, the new Congress.gov is an immense improvement on THOMAS in every way, as I reported last year:
Tapping into a growing trend in government new media, the new Congress.gov features responsive design, adapting to desktop, tablet or smartphone screens. It’s also search-centric, with Boolean search and, in an acknowledgement that most of its visitors show up looking for information, puts a search field front and center in the interface. The site includes member profiles for U.S. Senators and Representatives, with associated legislative work. In a nod to a mainstay of social media and media websites, the new Congress.gov also has a “most viewed bills” list that lets visitors see at a glance what laws or proposals are gathering interest online.
Since September 2012 digital staff at the Law Library of Congress have been busy since the Congress.gov launched in beta, adding new features and context at a steady pace, including adding the Congressional Record, committee reports, standing committee pages, and the ability to “Search within results.”
On November 19th, when THOMAS is retired, the social media outposts of the site will also transition. @THOMASDotGov will transition its more than 15,500 followers to a new identity.
Did you see @librarycongress news? http://t.co/svm8Yee3on will redirect to http://t.co/jzJSAfIx4v beginning Nov. 19 http://t.co/Kbk5mMQuy5
— THOMASdotgov (@THOMASdotgov) November 8, 2013
In a press release, the Library of Congress indicated that the old site will remain accessible from the Congress.gov homepage through late 2014. After that, historians may have to hope that the National Archives adopts whatever code or data retains historical interest into its servers, lest it moulder and succumb to bitrot — unfortunately, the configuration of the robots.txt file for Thomas.gov appears to have prevented the Internet Archive from preserving its iterations over the years.
If you’re interested in learning how to use the new Congress.gov, you can register at beta.congress.gov/help for training sessions scheduled for November 14, January 16, March 11 and March 16.

I wonder how much it cost.
According to the New York Times, the Library of Congress operating budget for this operating year is $598.4 million. That’s down from $629,207,000 in FY 2012, though, when much of the work of relaunch was done. Digging further into the 2012 financials for the LOC, however, I can’t find a single line item for IT expenses, much less this specific project. At least gives us a boundary condition.
When asked by the Washington Post last year, Library of Congress “web services chief” Jim Karamanis said that the “overhaul was funded within the regular operating budget.”
“There’s not really a way to put a number on it,” said Karamanis to the Post. “This is us doing our job.”
Pingback: News from the Library: Moving on from Thomas & myLOC - TPS-Barat Primary Source Nexus
Pingback: Intersect Alert November 11, 2013 | SLA San Francisco Bay Region Chapter